The department of Food Science was established in September 2010, under the Faculty of Food Technology. The team of lecturers includes 1 Ph.D., and 6 masters with experience, enthusiasm, and creativity in work.
The main tasks of the department are to train and manage the modules of the basic knowledge such as:
- A basic understanding of microbiology and biochemistry towards application in hygiene control and food safety.
- Basic knowledge of food technology.
The modules belonging to the base specialized knowledge such as:
- Food Chemistry
- Food Biochemistry
- Food Microbiology
- Food Biotechnology
- Microbiological Analysis
- And some laboratory modules: Food Microbiology Laboratory; food chemistry Laboratory, and Application of Biotechnology in Food Technology (Laboratory).
Besides training activities, the lecturers of the department always focus on scientific research and improve the quality of teaching. The main research directions of the department are:
- Development of probiotic supplement products
Probiotics help to inhibit harmful bacteria and return the balance of the intestinal microflora. Therefore, the addition of probiotics to the human body is very important. A lot of fermented foods such as yogurt, pickles, and fermented soybeans contain lots of good bacteria for the body...
Some fermented foods such as drinking yogurt, Kombucha (fermented tea), or Kefir (fermented milk drinks) are natural foods that contain many probiotics, good for the body.
.png)
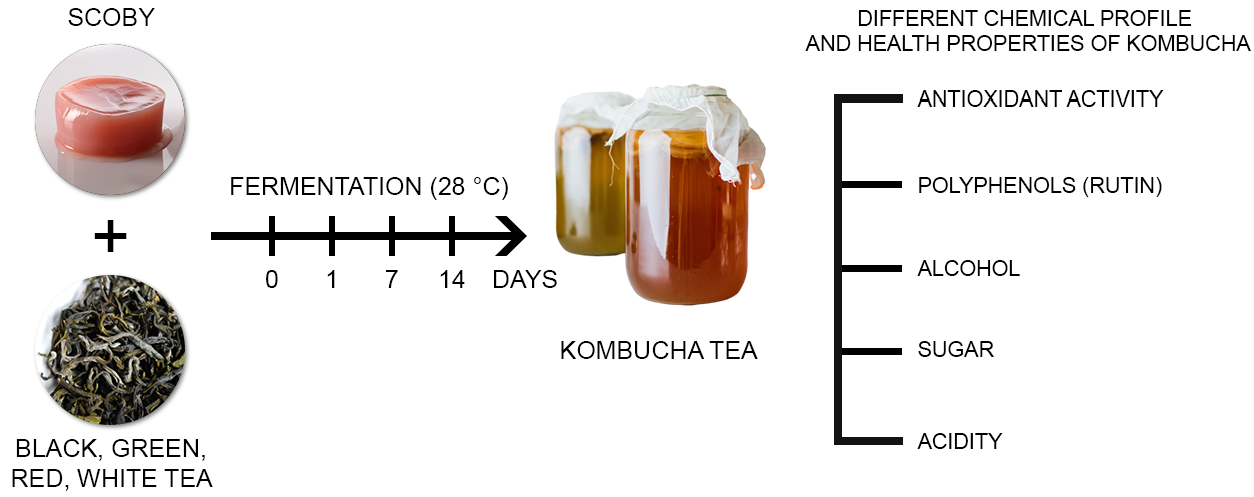
- Research and development of Kombucha products
Kombucha tea is not only a tea used for sipping, and refreshing but also a portion of food for many functions that benefit the health of users. Also known as 'immortal tea ', researchers have proven that Kombucha is effective in maintaining and restoring health through four main characteristics: detoxification, antioxidant, energy boost, and boosting the immune system
- Enzyme technology and its application in the food industry
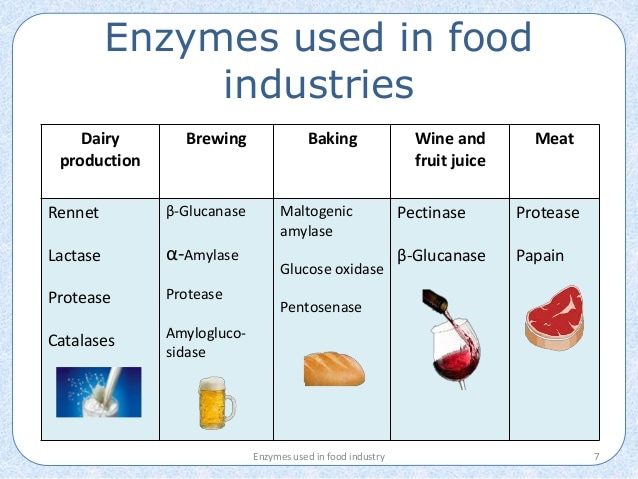
Enzymes are widely used in the food industry, which contributes to the diversity, abundance, and improvement of food product quality.
Enzyme protease is used in the meat processing industry for the purpose of softening meat, making food easy to digest, and producing hydrolyzed fluids containing much protein.
Enzyme renin and pepsin are utilized for coagulation in the production of cheese. In the production of fruit juice from crushed fruit ingredients, the enzyme pectinase makes the fruit juice transparent and easy to filter.
Enzyme cellulase helps to increase absorption, improve taste and soften a variety of plant foods, which helps improve food quality.
Enzyme amylase has been commonly used in some areas of the food industry, such as the production of bread, alcohol, beer, etc. In bread production, amylase has completely changed the quality of bread, including taste, color, Styrofoam, etc. Sugar maltose, commonly used in confectionery production, is a powdered glass product made of the enzyme amylase. Enzyme glucoamylase is a factor that increases efficiency in alcohol production. In beer production, the use of amylase in sprout seeds to replace malt has contributed significantly to the decline in prices.
- Mushroom Products
Edible mushrooms contain a lot of protein, low fat, and calories. Moreover, they also contain substances that are beneficial to humans such as polysaccharides, minerals, and smoothies. Mushrooms are fragrant, delicious foods with attractive smells containing a lot of free amino acids and unique aromatic compounds each mushroom, such as shiitake mushrooms with Guanosin 5’ - monophosphate that give off a unique aroma.
Mushrooms contain about 17-19 amino acids, of which there are 9 types of amino acids that cannot be replaced. According to literature data, nine common mushrooms, such as button mushrooms, shiitake mushrooms, enoki mushrooms, abalone mushrooms, wood-ear mushrooms, snow fungus, and monkey head mushrooms have a total amino acid content of 15.76% (based on dry weight), in which the content of non-replaceable amino acids was 6.43%, accounting for 40.53% of the total amino acid content.
Currently, some foods have been processed from edible mushrooms in order to directly provide the essential amino acids to the body, such as mushroom snacks, mushrooms salted shredded, dried mushrooms, or mushroom powder.